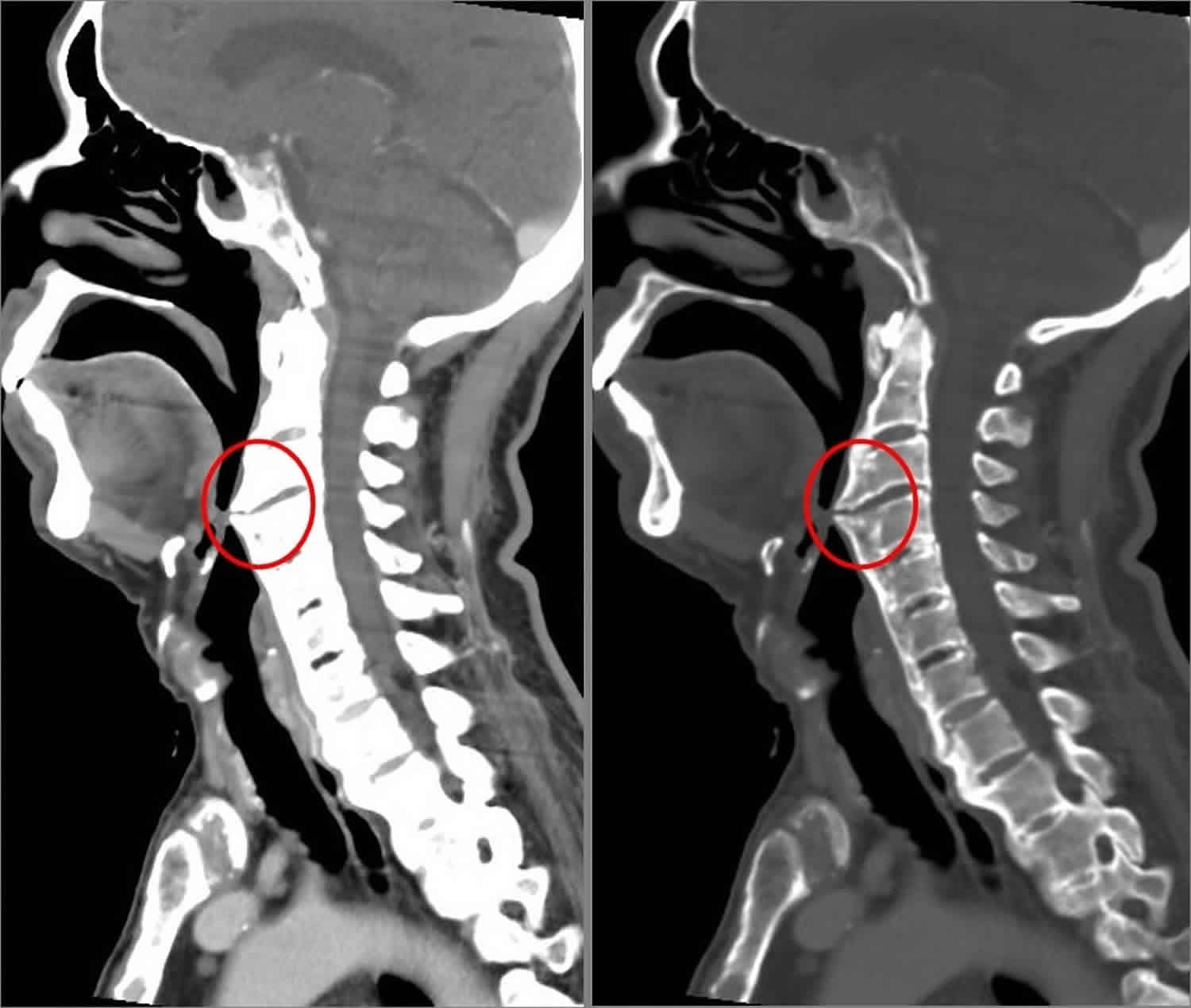
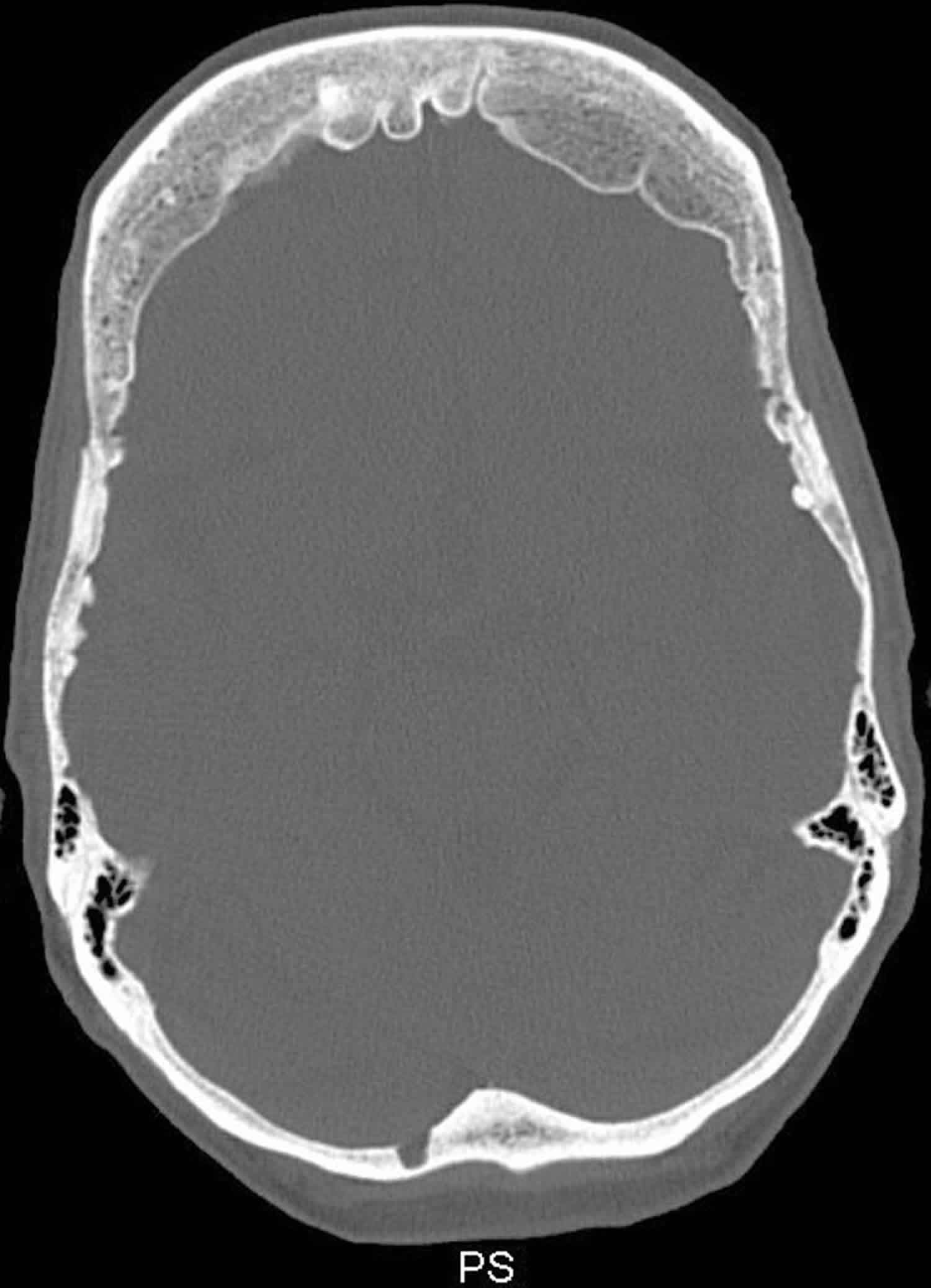
Hyperostosis is an excessive growth of bone. It may lead to exostosis. It occurs in many musculoskeletal disorders and from use of drugs like Isotretinoin.
Disorders featuring hyperostosis include:
- Camurati-Engelmann disease, type 2
- Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, primary, autosomal recessive, 2
- Melorheostosis
- Tumoral calcinosis, hyperphosphatemic, familial, 1
- Worth disease
See also
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
- Hyperostosis frontalis interna
- Infantile cortical hyperostosis
- Porotic hyperostosis
- SAPHO syndrome
References
- Stuart-Macadam P (April 1985). "Porotic hyperostosis: representative of a childhood condition". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 66 (4): 391–8. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330660407. PMID 3887936.
- Suri D, Dayal D, Singh M (July 2005). "Infantile cortical hyperostosis". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 90 (7): 711. doi:10.1136/adc.2004.065334. PMC 1720499. PMID 15970613.
- Hayem G, Bouchaud-Chabot A, Benali K, et al. (December 1999). "SAPHO syndrome: a long-term follow-up study of 120 cases". Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 29 (3): 159–71. doi:10.1016/S0049-0172(99)80027-4. PMID 10622680.
- MOORE S, CARR AD (January 1952). "Hyperostosis frontalis interna; two contrasting cases". Journal of the American Medical Association. 148 (3): 199–200. doi:10.1001/jama.1952.62930030004009b. PMID 14880497.
External links